IN THE SPOTLIGHT: MDE to MDB Conversion Service
(also supports: ACCDE to ACCDB, ADE to ADP, etc)
IN THE SPOTLIGHT: Access Database Repair Service
An in-depth repair service for corrupt Microsoft Access files
IN THE SPOTLIGHT: vbWatchdog
VBA error handling just got easier...

" vbWatchdog is off the chart. It solves a long standing problem of how to consolidate error handling into one global location and avoid repetitious code within applications. "
- Joe Anderson,
Microsoft Access MVP
Meet Shady, the vbWatchdog mascot watching over your VBA code →
(courtesy of Crystal Long, Microsoft Access MVP)
IN THE SPOTLIGHT: vbMAPI
An Outlook / MAPI code library for VBA, .NET and C# projects
Get emails out to your customers reliably, and without hassle, every single time.
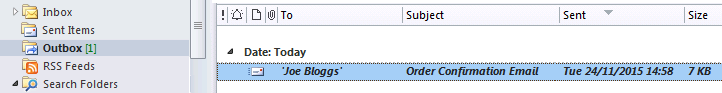
Use vbMAPI alongside Microsoft Outlook to add professional emailing capabilities to your projects.
IN THE SPOTLIGHT: Code Protector
Standard compilation to MDE/ACCDE format is flawed and reversible.
Provided by Allen Browne, allenbrowne.com, June 1997. Updated October 2004.
Every function or sub should contain error handling. Without it, a user may be left viewing the faulty code in a full version of Access, while a run-time version just crashes.
The simplest approach is to display the Access error message and quit the procedure. Each procedure, then, will have this format (without the line numbers):
1 Sub|Function SomeName() 2 On Error GoTo Err_SomeName ' Initialize error handling. 3 ' Code to do something here. 4 Exit_SomeName: ' Label to resume after error. 5 Exit Sub|Function ' Exit before error handler. 6 Err_SomeName: ' Label to jump to on error. 7 MsgBox Err.Number & Err.Description ' Place error handling here. 8 Resume Exit_SomeName ' Pick up again and quit. 9 End Sub|Function
For a task where several things could go wrong, lines 7~8 will be replaced with more detail:
Select Case Err.Number
Case 9999 ' Whatever number you anticipate.
Resume Next ' Use this to just ignore the line.
Case 999
Resume Exit_SomeName ' Use this to give up on the proc.
Case Else ' Any unexpected error.
Call LogError(Err.Number, Err.Description, "SomeName()")
Resume Exit_SomeName
End Select
The Case Else in this example calls a custom function to write the error details to a table. This allows you to review the details after the error has been cleared. The table might be named "tLogError" and consist of:
Field Name Data Type Description ErrorLogID AutoNumber Primary Key. ErrNumber Number Long Integer. The Access-generated error number. ErrDescription Text Size=255. The Access-generated error message. ErrDate Date/Time System Date and Time of error. Default: =Now() CallingProc Text Name of procedure that called LogError() UserName Text Name of User. ShowUser Yes/No Whether error data was displayed in MsgBox Parameters Text 255. Optional. Any parameters you wish to record.
Below is a procedure for writing to this table. It optionally allows recording the value of any variables/parameters at the time the error occurred. You can also opt to suppress the display of information about the error.
Function LogError(ByVal lngErrNumber As Long, ByVal strErrDescription As String, _
strCallingProc As String, Optional vParameters, Optional bShowUser As Boolean = True) As Boolean
On Error GoTo Err_LogError
' Purpose: Generic error handler.
' Logs errors to table "tLogError".
' Arguments: lngErrNumber - value of Err.Number
' strErrDescription - value of Err.Description
' strCallingProc - name of sub|function that generated the error.
' vParameters - optional string: List of parameters to record.
' bShowUser - optional boolean: If False, suppresses display.
' Author: Allen Browne
Dim strMsg As String ' String for display in MsgBox
Dim rst As DAO.Recordset ' The tLogError table
Select Case lngErrNumber
Case 0
Debug.Print strCallingProc & " called error 0."
Case 2501 ' Cancelled
'Do nothing.
Case 3314, 2101, 2115 ' Can't save.
If bShowUser Then
strMsg = "Record cannot be saved at this time." & vbCrLf & _
"Complete the entry, or press <Esc> to undo."
MsgBox strMsg, vbExclamation, strCallingProc
End If
Case Else
If bShowUser Then
strMsg = "Error " & lngErrNumber & ": " & strErrDescription
MsgBox strMsg, vbExclamation, strCallingProc
End If
Set rst = CurrentDb.OpenRecordset("tLogError", , dbAppendOnly)
rst.AddNew
rst![ErrNumber] = lngErrNumber
rst![ErrDescription] = Left$(strErrDescription, 255)
rst![ErrDate] = Now()
rst![CallingProc] = strCallingProc
rst![UserName] = CurrentUser()
rst![ShowUser] = bShowUser
If Not IsMissing(vParameters) Then
rst![Parameters] = Left(vParameters, 255)
End If
rst.Update
rst.Close
LogError = True
End Select
Exit_LogError:
Set rst = Nothing
Exit Function
Err_LogError:
strMsg = "An unexpected situation arose in your program." & vbCrLf & _
"Please write down the following details:" & vbCrLf & vbCrLf & _
"Calling Proc: " & strCallingProc & vbCrLf & _
"Error Number " & lngErrNumber & vbCrLf & strErrDescription & vbCrLf & vbCrLf & _
"Unable to record because Error " & Err.Number & vbCrLf & Err.Description
MsgBox strMsg, vbCritical, "LogError()"
Resume Exit_LogError
End Function
| Home | Index of tips | Top |
Rate this article: 




This is a cached tutorial, reproduced with permission.
TWINBASIC LTD (Company No. 16590181, VAT No. GB497509439)
Terms | Privacy | Sitemap | X (Twitter)